![DIY fail-proof content marketing strategy [eBook]](https://www.fronetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/content-marketing-strategy-1080x675.jpg)
by Fronetics | Jun 16, 2015 | Blog, Content Marketing, Marketing, Strategy

95% of B2B enterprise marketers and 86% of B2C marketers use content marketing. The down and dirty is that content marketing works. Content marketing attracts leads and converts leads to customers – and it does so at a lower cost than traditional marketing (and in a much less invasive manner). Here are some cold hard stats:
- 80% of business decision-makers prefer to get information from articles rather than through advertisements
- Inbound leads cost 60% less than outbound leads
- Adopting an inbound strategy doubles average website conversion rates, from 6% to 12%
The reality is that content marketing works. Customers are no longer responding to interruption-based marketing as they once did. They’re ignoring overt sales pitches and looking instead to peers, social networks, and search engines. In short, it’s all about content these days. Companies within every industry – from fashion to fishing – are creating and curating relevant and valuable content and using it to engage prospects and connect with customers.
We have created a DIY fail-proof strategy for connecting with prospects and building brand awareness by creating and distributing amazing content – our content marketing eBook. Earn the attention of your prospects and customers by using this checklist to develop a solid content marketing strategy. In it, you’ll find step-by-step instructions, templates, lists, and samples to get your content marketing program up and running.


by Fronetics | Jun 15, 2015 | Blog, Content Marketing, Data/Analytics, Marketing

It’s impossible not to recognize that the business world is changing. Whether it’s the fall of the travel agent as people migrate towards online booking, or the irrelevance of the compact disc as Spotify and iTunes changed the music industry, or how advertising is done. Outbound marketing, such as print ads, TV ads, banner ads, trade shows, telemarketing, and direct mail are no longer what consumers are requiring. According to Forbes, many brands are moving their advertising budgets from television to online videos. The Content Marketing Institute reports that 8 out of 10 people identify themselves as blog readers, and 23% of all time spent online is spent on social media sites. With the rise of the blog, companies have gotten smart about how to reach their current and potential consumers.
In the B2B world things are changing, too, with many executives wanting to gain information through other mediums. The Content Marketing Institute also reports that a majority (80%) of business decision-makers prefer to get information from articles rather than through advertisements.
We know that inbound marketing is effective in garnering consumers’ attention. It’s aligned with a generation of people who want to be educated about the products they’re buying and who are willing to search for those products online. Even with all of this known, it’s important to ask: what is the ROI when it comes to content marketing?
According to Search Engine Journal, inbound leads cost 60% less than outbound leads. In the Harvard Business Review article, How to Profit from “Lean Advertising”, the shoe company DC Shoes is profiled as a model for inbound marketing. In an industry where star athletes are profiled in big-production advertisements via TV commercials, billboards, and magazine ads, the skateboard shoe company decided to take a different route. According to the 2013 HBS article, “Over the past four years they have gotten more than 180 million views—and in 2011 alone, sales jumped 15%. One was YouTube’s most-shared video of 2011; another garnered a million views in its first 24 hours. Paying online media for this type of exposure would cost upward of $5 million.”
Like any new tack in business decisions, relying on case studies from other businesses is helpful, but cost needs to be considered. In order to calculate ROI the cost of content marketing needs to be assessed:
- salaries (if going in-house)
- marketing agency or contractor services
- additional overhead
- distribution costs
- design and publication software
After those costs have been calculated, the next step is to subtract that number from the revenue generated. The Guardian has put forth its simple content marketing ROI calculator:
(Revenue Generated – Cost of Content Marketing) / Cost of Content Marketing = ROI
According to the newspaper, “A simple calculation could say that you drove 1000 visits through a piece of content, and Google Ads would have cost £1 per click, e.g. £1000 to equal the same. If the content only cost £500, you have a saving!”
But with most seemingly simple things, there’s complexity underneath. Dig deeper and ask more questions. Is the money you’re spending on inbound marketing deterring other, less obvious, costs? Would it have cost you more through outbound marketing methods to achieve that same level of visibility than through inbound marketing solutions? Is inbound marketing bringing in customers or closing a deal more quickly than alternative methods (time is money, after all)? Is inbound marketing cutting down the need for staffing in other areas, such as support staff to manage inquiries or support calls?
Some incalculable values from inbound marketing, like consumer preferences, content intelligence, customer relationship strategies, and branding can be hard to tie to a number, but over time you will see that your ROI will become more clear to you as you generate leads, turn leads into customers, and see the result in the form of money gained (American dollars or British pounds!).

by Jennifer Hart Yim | Jun 11, 2015 | Blog, Content Marketing, Marketing
This is a guest post written by Thijs Messelaar. Thijs has more than 15 years’ experience writing, developing content, and informing marketing strategy for various clients, including high tech, higher education, and highly-rated restaurants.
 The best content marketing feels like a great story.
The best content marketing feels like a great story.
In fact, in many ways content marketing gets the most results because it IS a great story. It captures your imagination. It challenges you. It asks for your trust. And, if it’s truly tops, the payoff is big.
In order to get results from your content, a solid content marketing strategy must be in place. No doubt about it. Simply just creating incredible content and walking away from it probably isn’t going to get you what you want.
Key Content Marketing Channels
Content marketing requires a careful scientific approach in order to get results. Content needs to be curated, cajoled, packaged, posted, pruned, repurposed, prettified, shared, shorn, shifted, pushed out, and run up the flagpole.
To get results from your content, your content will have to be created for and/or distributed through key marketing channels like these:
- Your website assets
- Blog
- Landing pages
- Case studies
- Team (clout)
- Accolades and awards
- Resources
- Videos
- Surveys and quizzes
- Infographics
- E-books
- White papers
- Email
- SEO (onsite)/SEM (AdWords)
- Apps
- Social media (organic)
- Retargeted ads (web and social media)
- Social media ads, promoted posts, offers
- Webinars, trainings, and mini-courses
- Podcasts (audio and video)
You need to organize and optimize your sales pipeline by identifying your goals, audience, and your content marketing channels. And like a good scientist, you’ll have to analyze your results and revise your approach, over and again and again.
Examining all aspects of your content marketing strategy – creation, distribution, engagement – on your content marketing ROI is essential.
The Magic of Content Marketing
But without producing the most interesting, the most useful, the most delicious writing, design and ideas to place in these various channels, your content marketing will be dead in the water.
Great content marketing moves you to do something new and unfamiliar. Or it makes you understand something familiar in a new way. And like a really good story, you want to share good content with everyone. It’s affirming (or reaffirming) and engaging and makes you feel its magic. The magic of content marketing that gets results may be found in the sense of clear authority it imparts.
But the magic of a great story is something intangible. It comes from a true place within you (your soul, let’s say) – and connects with your audience (their souls).
But much of the best content marketing is built on novel, engaging, social, physical, and emotional experiences – not solely on rote data analysis.
Douglas Van Praet advances this relatively controversial take on current marketing practices. “We need to generate smiles, tears, or goose bumps—not significant differences correlated at the 95% confidence interval! These are the things that […] data tabulations will never capture, but they are also the things that make us buy brands,” he writes.
Likewise, these key content marketing attributes are also the essential characteristics of our most favorite and enduring stories.
If yours is merely content created for the sake of just churning more content – that is, if you don’t care much for what you’re writing about – your audience won’t care much either. It will curdle the moment they consume it.
Without moving your audience emotionally, you won’t have excited them intellectually, you won’t have made them care about you or gained their valuable (and venerable) trust. And surely your audience won’t hold your story “near-and-dear” to their hearts in a way that compels them to retell it to everyone and anyone who will listen.
The overall result? Well, poor results from your content marketing and ultimately a weakening of your brand’s standing.
Start your content creation from the soul by being yourself and talking about what you love. You’ll make connections and grow your audience just as the best storytellers have always done.
In the end, you’ll succeed with content marketing in ways you never might have imagined possible – and feel good doing it.
That in itself will be a story worth telling.
by Fronetics | Jun 10, 2015 | Blog, Logistics, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy, Supply Chain
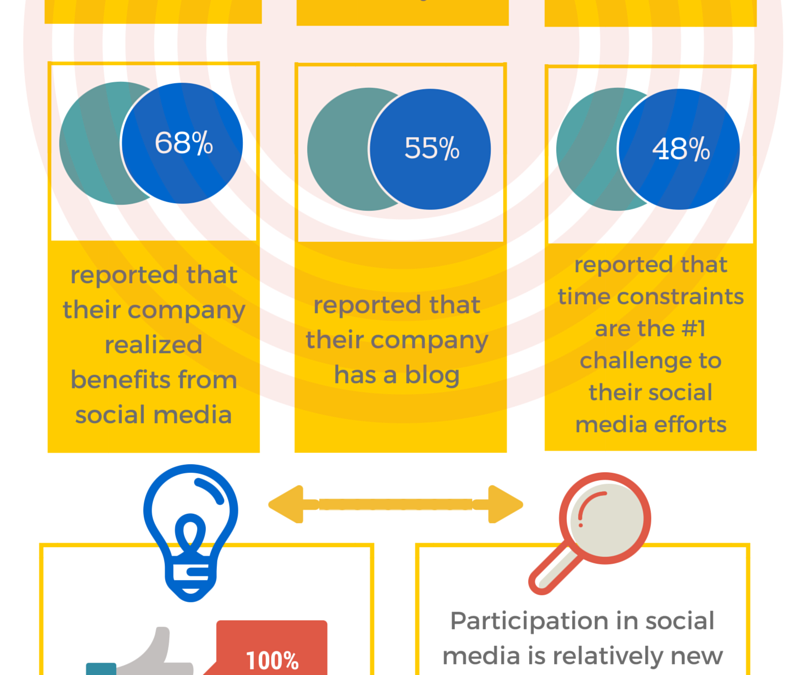
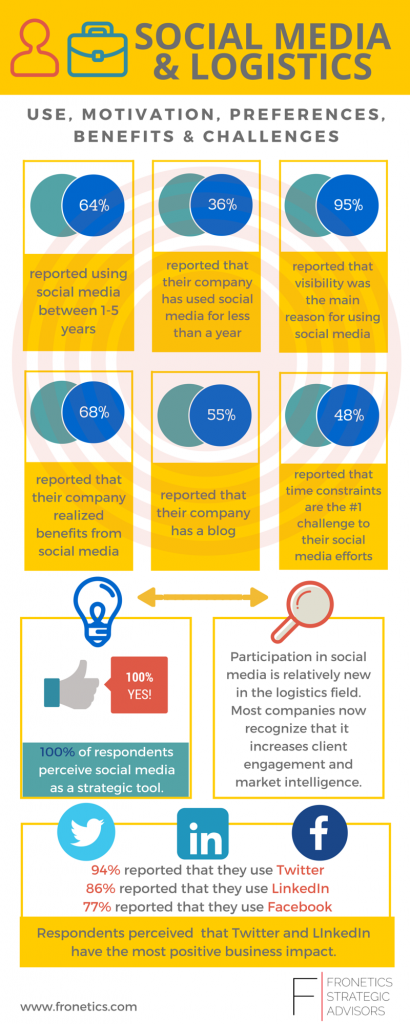
Fronetics Strategic Advisors conducted a survey focusing on social media and logistics and supply chain companies. Respondents shared information on their social media use, motivation, preferences, benefits, and challenges. One-hundred percent (100%) of respondents reported that they have used social media for five years or less, indicating that social media is a relatively new strategy for logistics and supply chain companies. Mirroring other industries, including those in Fortune 500 status, social media is playing an increasingly important role in company branding, marketing, and client engagement.
For the current state of social media and logistics, here is an infographic that summarizes many of the key points from the full report.
by Fronetics | Jun 9, 2015 | Blog, Logistics, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy, Supply Chain

Transfix is poised to disrupt and transform the trucking industry.
Uber, the on-demand driver for hire mobile service, has come to stand for disruption. The company has not only transformed the taxi industry, it has changed everything. Uber, Aaron Levie notes, is a “lesson in building for how the world *should* work instead of optimizing for how the world *does* work.” NY-based start-up Transfix is doing just this. With the launch of the company’s new app, Transfix is poised to disrupt the trucking industry.
The trucking industry is huge. Valued at $800 billion, the industry moves the majority (67%) of freight tonnage in the US. To move this volume of freight, more than 3 million trucks log close to 100 billion miles annually. It is, therefore, not surprising that “truck driver” is the most common job across the US. What is surprising is that the industry is riddled with inefficiencies. One of the greatest inefficiencies has to do with needless miles. Drew McElroy, co-founder of Transfix, estimates that U.S. commercial trucks drive 19 billion needless miles each year. That’s a lot of needless miles.
Together, the industry’s inefficiencies have a significant impact not just on the bottom line, but also on the cost of goods, the environment, our country’s infrastructure, traffic, and on the truck drivers themselves.
 Transfix takes the industry’s inefficiencies head on. Transfix is a digital on-demand freight marketplace. It provides industry-leading mobile technologies and location-based jobs offers for independent over-the-road truck drivers, as well as cloud-based management platforms for small carriers and shippers.
Transfix takes the industry’s inefficiencies head on. Transfix is a digital on-demand freight marketplace. It provides industry-leading mobile technologies and location-based jobs offers for independent over-the-road truck drivers, as well as cloud-based management platforms for small carriers and shippers.
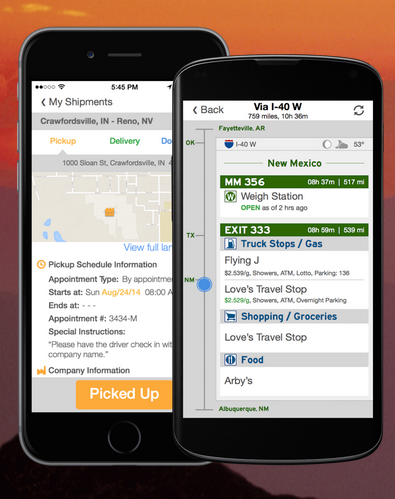
Transfix’s app integrates with the company’s digital marketplace and is driver-centric. The app gives drivers the ability to manage loads, map their itinerary, and manage payments. The app also provides truck drivers with trip planning essentials including the location of showers, ATMs, weigh stations, fuel prices, and weather.
The app is available for iOS and Android.
Barnes and Noble is one of Transfix’s early adopters. According to McElroy, Barnes and Noble has realized improvements in their processes and has seen their deadhead runs (times driving without cargo) cut by at least 50%.
Transfix co-founders Drew McElroy and Jonathan Salama have identified how the trucking industry should work and have provided industry stakeholders with the tools to make it happen. Transfix is poised to disrupt and transform the trucking industry. With Transfix, we are witnessing the Uberfication of trucking.

by Fronetics | Jun 8, 2015 | Blog, Manufacturing & Distribution, Strategy, Supply Chain

For many years robots seemed like the brainchild of science fiction writers and directors, meeting the needs of humans as we saw in the Jetsons, or challenging them as we saw in Battlestar Galatica. Occasionally we hear stories on the news of robots being built in basement labs at prestigious universities such as MIT or Stanford. Recently there was a report on NPR about how one of UCal Berkeley’s robots couldn’t easily figure out how to fold laundry, so, one could ask: what are we worried about? If robots can’t fold laundry in under ten minutes, could they take over manufacturing?
There has been a downward trend in manufacturing jobs since 1980 in the U.S. with similar spirals in Japan, Germany, and China. Is there a correlation between the decrease in manufacturing employment and the rise of the robot? According to the Wall Street Journal, in 2014 most industrial robots were operating in the same countries/regions: Japan (306,700 robots), North America (237,400), China (182,300), South Korea (175,600), and Germany (175,200).
In the same WSJ article, a new generation of robots is profiled. These robots are “smarter, more mobile, more collaborative, and more adaptable.” They are also less bulky and less dangerous for humans to work next to. One might say that the newest generation of robots is acquiring many of the positive qualities of human workers, and that that, combined with many skills humans don’t and can’t possess, makes them the ultimate worker. If robots supersede the work humans can physically do, in a faster, safer, more efficient way, then what will come of the human worker?
Many believe that robots will allow for manufacturers to return to the U.S. from their low-paying, cost-saving plants overseas. They also believe that robots won’t take away from jobs, but rather create them. According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), robots actually create millions of jobs. The IFR’s reports oppose the idea that manufacturing jobs are waning. In 2011 article Positive Impact of Industrial Robots on Employment, the author, Metra Martech, stated, “The German and Japanese (automotive) manufacturers who have invested heavily in automation and robots have maintained a lead in the quality market. Germany has increased the number of people employed in the automotive sector.”
The IFR also states that there are many other benefits to robots in manufacturing:
- robots carry out work in areas that would be unsafe for humans.
- robots carry out work that would not be economically viable in a high wage economy.
- robots carry out work that would be impossible for humans.
“The Second Economy”, one in which computers have business interactions only with other computers, is upon us. According the to economist, Brian Arthur, who coined the term, things might not look so bright for the future of the American worker. He states, “If the Second Economy does achieve that rate of growth, it will be replacing the work of approximately 100 million workers. To put that number in perspective, the current total employed civilian labor force today is 146 million. A sizeable fraction of those replaced jobs will be made up by new ones in the Second Economy. But not all of them. Left behind may be as many as 40 million citizens of no economic value in the U.S alone. The dislocations will be profound.”
Others, some who are at the forefront of technology, are also very concerned about the rise of robots. Apple co-founder, Steve Wozniak, is one of the worried. He was recently quoted saying, “Computers are going to take over from humans, no question… Like people including Stephen Hawking and Elon Musk have predicted, I agree that the future is scary and very bad for people. If we build these devices to take care of everything for us, eventually they’ll think faster than us and they’ll get rid of the slow humans to run companies more efficiently.T”
The stuff of sci-fi is becoming a reality. As we humans make the robots that will replace us, only time will tell if that will benefit our race or harm it.
![DIY fail-proof content marketing strategy [eBook]](https://www.fronetics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/content-marketing-strategy-1080x675.jpg)









