
by Fronetics | Oct 27, 2016 | Blog, Content Marketing, Marketing, Social Media, Strategy
Company X also saw web traffic grow by 180% in 90 days by using Google AdWords and Facebook Ads.
Sometimes our clients can be a little hesitant to try pay-per-click advertising. Take Company X, for example.
Company X’s target customer fits a very particular profile, in terms of geography, income, and age. Because of those specific demographics, the client was not confident that a pay-per-click advertising campaign would be an effective way to reach those target customers. But we thought differently.
When paired with a content marketing program, pay-per-click can be one of the cheapest, in terms of cost-per-lead, and most efficient ways to reach a target audience. Thus, we convinced Company X to try PPC on a trial basis, investing just a small budget.
We developed a strategy for the client, using Google AdWords and Facebook Ads. Over the course of 90 days, the results were phenomenal.
A few key results:
- Company X acquired 54 leads.
- Traffic from paid search grew by 180%.
- The lead-to-customer conversion rate was nearly 3x the industry standard.
Needless to say, Company X will be expanding the use of pay-per-click advertising in the future.
How can pay-per-click help your business?
PPC can seem intimidating to the novice. But, when done right, it can be a highly effective way to reach the very specific kind of customer your business is looking for. A little bit of know-how can be all the difference.
As such, Fronetics has developed a quick training on the basics of pay-per-click advertising: what it is, what platforms are available, etc. If you are interested in learning more about PPC and how it might complement your marketing program, download our free guide below.

Related posts:

by Fronetics | Oct 26, 2016 | Big Data, Blog, Content Marketing, Data/Analytics, Marketing
Big-data insights can help you segment your email database to better target prospects based on where they are in the buyers’ journey.
Most companies these days are swimming in a sea of big data, the great swaths of information they’ve amassed from sales records, social media connections, website leads and contacts, and online analytics.
At first glance it’s a tangle of information that is hard to organize and even harder to learn anything from. That’s a stumbling block that forward-looking businesses need to overcome. Big data can help breathe new life into one of the most reliable yet shopworn tools of the trade: email campaigns.
Embrace Big Data
A study by the executive head-hunting firm Spencer Stuart surveyed 171 companies regarding big-data usage. Just a little over half of the companies used their big data to help guide email, SEO, and SMS marketing campaigns. That’s a fairly low rate, given the potential leg-up that big data can provide.
Consider what Walmart is doing. The company has big-data information on about 60% of all Americans, with which it micro-targets customers based on their individual interests and habits. It’s a powerful strategy that is spreading quickly to businesses of all sizes.
How can you use big data to freshen up your email campaigns?
Be a Collector, Not a Hoarder
Chances are, you are obtaining a lot of data, especially if you have an active content marketing plan in place. Not all of the data you get is equally important. Your focus should be on data that can lead to an actionable and quick response — for example, are you gathering information on your customers’ buying habits? Do you know who they are, where they are, what their interests are, what their email address is, and how your business connects with them?
Collect that relevant data and study it. Much of it will come from the buyer’s journey — the breadcrumbs that potential buyers leave for you in your big data. These pieces of information are keys to your personalized email responses.
Respond In Kind
Most experts agree that a quick and targeted email response is a good strategy for encouraging a new customer to make a purchase. The email needs to respond directly to the buyer’s interests — using information you’ve (hopefully) logged with your big data.
From this point on, it’s crucial to make sure that every email that is sent to that buyer is built around a backbone of big data. Nurture your customers with personalized emails that offer content and deals that line up with their specific interests.
Don’t Mess with the Masses
Mass emails — the generic sales pitch email — used to be the cost-effective and simple way of reaching and converting customers. Now, it’s more than likely they’ll get sent to the trash, or worse, the spam filter. The mass email is your one-way ticket to spam purgatory.
“Traditional methods of mass marketing doesn’t resonate anymore and they’re being ignored by the audience,” said Volker Hildebrand, Global Vice President of Strategy at SAP Hybris, in a recent interview with Forbes. “Data is the fuel for customer engagement, and being able to pull together all the relevant information about in real-time.”
You can do better than the mass email approach. If you’ve collected relevant data and you’ve studied your buyers’ journeys, you have the tools in place to build a smart email campaign. Tailor your campaign to personalize your approach to your customers, and more than likely they’ll open that email.
Related posts:

by Fronetics | Oct 25, 2016 | Blog, Strategy, Talent
A reduced workweek may mean better performance, talent retention, and bigger payoff for employers.
In August 2016, the Washington Post reported that Amazon plans to pilot a program in which select teams will work just 30 hours a week. The teams’ employees will be salaried and receive full benefits, as well as 75% of the pay full-time employees earn. The entire team, including managers, will work on this reduced schedule.
“We want to create a work environment that is tailored to a reduced schedule and still fosters success and career growth,” states an event posting by the company. “This initiative was created with Amazon’s diverse workforce in mind and the realization that the traditional full-time schedule may not be a ‘one size fits all’ model.”
The program comes just a year after a New York Times report depicted Amazon encouraging marathon workweeks while discouraging vacation — and even unfairly evaluating employees in the wake of personal crises like cancer or miscarriages.
Will the new part-time program help combat that image? Will the 30-hour workweek model impact Amazon’s productivity? While Amazon does not plan to roll the program beyond the select teams, research suggests that the company might reap some positive benefits from employees’ working less.
A reduced workweek benefits employees and the employer
Let’s look at how working fewer hours might result in healthier, more productive employees.
1. Shorter hours improve the physical and emotional health of the worker.
A National Bureau of Economic Research study examined manufacturing companies that experienced an unexpected spike in exports, meaning longer working hours, and the resulting toll on employees. The findings revealed that long hours on the job increase an employee’s risk for heart attack, depression, and injury. But despite more health concerns, employees took fewer sick days. The impact on productivity when a company has more sick, injured workers is self-evident.
On the contrary, a shorter workweek correlates with better physical, mental, and emotional well-being. That translates to more alert, adjusted, happy employees who have more stamina to complete their jobs. In fact…
2. A reduced workweek does not decrease productivity — rather, it often increases it.
There’s a reason 43% of companies offer shorter workweeks to some employees: It has a positive impact on their bottom lines. Just how much? Tax services firm Ryan saw revenue and profits almost double and client satisfaction reach an all-time high. KPMG goes as far as to say it uses flexible work hours as a “strategic business tool” that “allows us to accomplish our business goals and become more successful.”
Well employees leading balanced lives are able to accomplish more in a shorter amount of time, and that pays off for their companies.
3. Shorter hours may increase employee engagement and decrease turnover.
All the extra hours workers are putting in actually drive disengagement. Left wholly left unchecked, the culmination of issues arising from an unbalanced work-home life can increase absenteeism and turnover. Simply put, employees logging long hours are significantly more prone to burnout.
And turnover can be costly for employers. The U.S. Department of Labor currently estimates the average cost of a bad hiring decision to be as much as 30% of an individual’s first-year potential earnings. Think about how that adds up as employees put more time with the company and earn higher salaries.
Going back to Ryan, the tax services firm, implementing a shorter workweek reduced the company’s turnover rate from 30% to 11%. That’s huge.
So, Amazon is definitely onto something with its 30-hour workweek experiment. The question is, what will happen when it succeeds? Will more businesses try reducing working hours? Could something like this work for your business?
Related posts:

by Fronetics | Oct 20, 2016 | Big Data, Blog, Data/Analytics, Logistics, Manufacturing & Distribution, Strategy, Supply Chain, Warehousing & Materials Handling
These industry leaders are leveraging insights from big data to solve business problems and drive profitable customer action.
Big data is more than just a buzzword: It’s helping companies make big-impact business decisions based on customer behaviors, purchasing patterns, and preferences.
Not all organizations have the resources to invest in big data. But for those that do, the payoff can big significant. The trick, of course, is knowing which numbers to analyze, what can be predicted, how to use big data for your particular business needs.
Let’s look at five big brands that are leveraging big data successfully to drive profitable customer action.
How 5 big brands use big data
1. Amazon
Amazon’s free same-day delivery service, Prime Now, allows Prime members to shop for over 25,000 products that can be delivered to their doorsteps within two hours. How can Amazon accurately predict the specific wants of millions of people across the country at a given time to prepare local inventory for immediate delivery? Aside from efficient warehousing and logistics, the company uses data on purchase history to optimally locate and stock its warehouses. This strategy also helps to reduce the time inventory stays in stock, diminishing working capital requirement.
2. Starbucks
Have you ever wondered how two neighborhood Starbucks locations can both stay in business? The company examines data on local traffic, demographics, and customers to determine the potential success of a new location before expanding. Starbucks can then choose to open a new store where it would be most successful, even if it’s just a few blocks from one of their other locations.
3. Walmart
In preparation for Hurricane Sandy, Walmart analyzed historical sales data before expected inclement weather and found an uptick in sales of flashlights, emergency equipment, and — to everyone’s surprise — strawberry Pop-Tarts in several locations. The company has since leveraged timely analysis of real-time data to drive business performance. As Walmart Senior Statistical Analyst Naveen Peddamail told Forbes: “If you can’t get insights until you’ve analysed your sales for a week or a month, then you’ve lost sales within that time. Our goal is always to get information to our business partners as fast as we can, so they can take action and cut down the turnaround time. It is proactive and reactive analytics.”
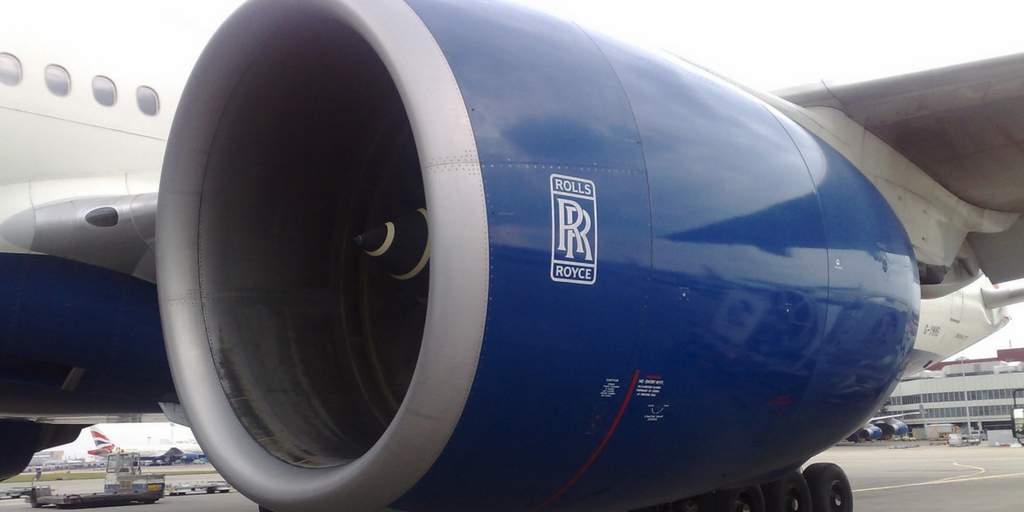
4. Rolls-Royce
Rolls-Royce has implemented big data processes in three key areas of their operations: design, manufacture, and after-sales support. Each design simulation for one of their jet engines, for example, generates tens of terabytes of data, which computer systems analyze to determine the viability of the design. The company’s manufacturing systems are increasingly moving toward a networked, Internet of Things (IoT) industrial environment. And after-sales support is completely changed by big-data analysis. Expert engineers continually examine real-time analysis from sensors fitted to all Rolls-Royce engines and propulsion systems to diagnose faults and mitigate issues.
5. Capital One
Big data helps Capital One determine the optimal times to send particular customers certain offers. The team analyzes demographic data and spending habits of their customers to optimize their offerings, which has increased conversion rates on their offers and generated more leads from their marketing budget.
How does your business use big data?
Related posts:

by Fronetics | Oct 19, 2016 | Blog, Content Marketing, Marketing, Social Media, Supply Chain
Native advertising is the non-ad-like way to promote your business’ content to users who might be interested in it.
Is your business using native advertising to promote your content with a targeted audience? If not, you’re missing out on one of the biggest upcoming trends in content marketing.
So how can your business use this technique to promote your content and, ultimately, your products and services? Let’s take a look at the basics of native advertising.
What is native advertising?
Native advertising blurs the line between advertising and editorial content. It allows publishers (of content) to get their message to a targeted audience in a format the audience is already using. Think of sponsored updates on LinkedIn, which look just like regular posts, or when a radio DJ promotes a product within the regular broadcast.
Content Marketing Institute founder Joe Pulizzi defines native advertising with the following three qualities:
- “A Directly Paid Opportunity. I hate to bring out the obvious, but native advertising is ‘pay to play.’ If a brand or individual did not pay for the spot, it’s not native advertising.
- “Usually Content Based. The information is useful, interesting and highly targeted to the specific readership. So, in all likelihood, it’s not an advertisement promoting the company’s product or service directly.
- “Delivered In-Stream. To truly be a native ad, the user experience is not disrupted. The advertising is delivered in a way that does not impede the normal behavior of the user in that particular channel.”
Native advertising is not content marketing…
… But it can be an effective way to promote your content.
Remember, content may be king, but distribution is queen, and she wears the pants. That is to say: Publishing valuable and relevant content in a strategic and consistent manner will create demand for your products and services. But content doesn’t go far — actually it goes nowhere — without distribution.
Native advertising is a paid opportunity to distribute your content to more people. It can be more effective than non-native advertising, like banner ads or commercials, because it does not interrupt the user experience but rather complements it. It doesn’t feel like an ad, even though someone paid to have it appear on your screen.
Social media platforms are offering more and more opportunities for businesses to advertise this way through sponsored posts and updates. LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest — you may have noticed that more and more posts from companies you don’t follow appear in your newsfeeds now. These platforms use proprietary algorithms to help businesses target users might be interested in the content they are promoting.
Here’s what a sponsored post on LinkedIn looks like, for example:
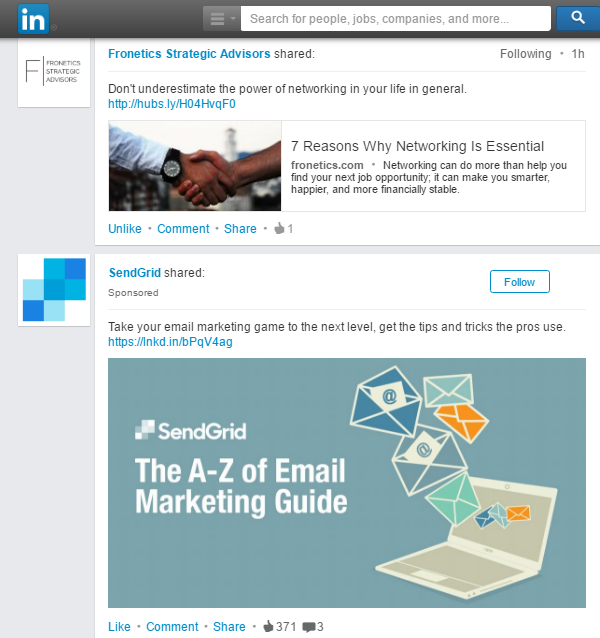
The sponsored post from SendGrid looks just like the other posts in my feed. Another important thing: It’s totally relevant for the kind of content I consume. I might even ignore the comma splice and click on it to get the information about email marketing because that’s what I like to read about on LinkedIn.
Some native advertising facts
The use of native advertising is growing among businesses because it is proving to be so effective. Here are some facts that might interest you.
Doing it right
Because native advertising blurs the line between editorial and advertising, some advertisers have gotten in trouble for violating rules of compliance. In response, the FTC has come out with some official guidelines for native ads in order to prevent confusion and to protect consumers. If your business is launching a native advertising campaign, make sure that you are familiar with these rules and best practices.
Related posts:







